Material Compatibilities
Our friction stir welding, machining, and engineering capabilities make us a market leader in producing high end fabricated structures.

Aluminum
Aluminum is one of the most common metals to friction stir weld because it has low weight, good corrosion resistance, and is easily welded. When aluminum is combined with alloying elements it can produce a range of useful mechanical properties.
1XXX aluminum alloy is almost pure aluminum and has low mechanical strength, high ductility, excellent corrosion resistance and high electrical conductivity. While fusion welding works for aluminum alloys, friction stir welding is a much better alternative.
2XXX aluminum alloy is composed of aluminum and copper. This alloy is useful in high-strength sheet or plate aerospace applications. It is extremely sensitive to hot cracking, and therefore un-weldable by fusion techniques. However, it is readily weldable using friction stir welding.
3XXX aluminum alloy is made up of aluminum and manganese. This alloy is a medium-strength aluminum alloy. It is very formable and often used for heat exchangers and air conditioners. Alloys of this series have moderate mechanical strength, high ductility and excellent corrosion resistance. The 3XXX aluminum alloy is easily friction stir weldable.
4XXX aluminum alloy is composed of aluminum and silicon. The 4XXX series alloys are most often encountered when they are being used as filler material within the welding or brazing processes, however this alloy is still able to be friction stir welded.
5XXX aluminum alloy is made of aluminum and magnesium. This alloy is used for high-strength sheet and plate alloys in marine applications, and is especially useful for building ships. 5XXX series alloys have excellent fusion weldability, but using fusions welding creates a large reduction in strength so a thicker material is needed to get the same strength. The friction stir welding process does not reduce strength and is a more cost effective solid state joining solution.
6XXX aluminum alloy is composed of aluminum, magnesium, and silicon. This alloy is useful for extrusions, large sheets, and plates. 6000 series aluminum alloys can be tricky to weld because they are prone to cracking, but with friction stir welding this issue does not exist, and they are readily weldable.
7XXX aluminum alloys are made of aluminum and zinc. This is especially useful for high-strength aerospace applications. These alloys are mostly unweldable due to their susceptibility to hot-cracking and stress-corrosion but are easily weldable using friction stir welding.

Copper
The high thermal and electrical conductivity of copper have made it a difficult material to weld in the past, particularly in thick sections. As FSW does not melt the material and applies mechanically generated heating locally, it has been a useful process for welding copper.
Applications in copper alloys include the welding of copper cold plates and heat sinks and the fabrication of brass and bronze components, including propellers and impellers, for marine applications. Brass can also be friction stir welded and used in other architectural applications.

Magnesium
In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in the use of magnesium parts for automotive components, usually made by pressure die casting. These have limited ductility, contain gas occlusions, and are frequently difficult to weld by fusion welding techniques. The solid state joining technique of friction stir welding produces excellent, low-cost, high-integrity welds in aluminium, and created a large demand for the process to be adapted for welding magnesium. Some benefits of using friction stir welding on magnesium are the stiffness to weight ratio, low density, and high damping capacity.

Ferrous Metals
There are numerous benefits associated with the friction stir welding of steel such as reduced distortion, reduced rework costs, enhanced weld properties, the ability to weld steels that are difficult or impossible to weld by other techniques, reduced labor, training and certification costs, and reduced energy consumption.
In addition to the single-material welds such as carbon steels and stainless steels, it is possible to weld dissimilar grades of steel. Friction stir welding steel has many applications across many industries. Steel is commonly used in the marine and automotive industries to make high strength steel panels.
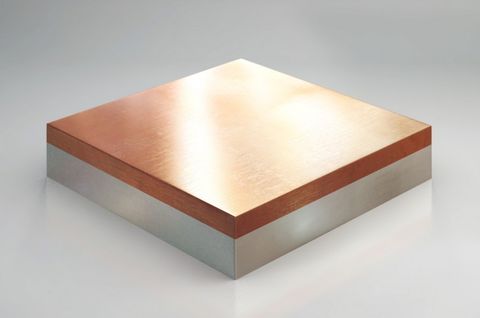
Dissimilar Materials
As FSW is a solid-state process that mechanically stirs metals together to form a bond between them, it can be used to join dissimilar metals. This is most easily achieved when the metals to be joined have similar thermal properties and melting temperatures. While fusion welding does not allow for dissimilar alloys or metals to be welded together, dissimilar alloys such as 2xxx and 7xxx aluminum alloys can be welded together using friction stir welding. Using friction stir welding, dissimilar metals can also be joined together such as aluminum and copper. This is especially useful in the automotive and electrical industries. Dissimilar metal welding finds great use for applications such as the manufacturing of batteries, fine wires, fuel cells and even medical devices. Dissimilar metal welding is also great for other applications in the aerospace and thermal management industries as well.
